Getting Started
Hello Mnexium!!!
In this getting started guide, we'll build a fully functional ChatGPT clone with persistent memory and conversation history — all in under 200 lines of code. The complete example is available on GitHub.
Marius Ndini
Founder · Jan 1, 2026
Building AI applications with persistent memory has traditionally been complex. You need to manage vector databases, handle embeddings, implement retrieval logic, and maintain conversation history. Mnexium simplifies all of this into a single API call.
What would normally require weeks of infrastructure work — setting up PostgreSQL with pgvector, writing embedding pipelines, building retrieval logic, and managing conversation state — took us less than an afternoon with Mnexium.
Why Mnexium?
When building AI chat applications, you quickly realize that the hard part isn't the AI — it's everything around it. Here's what Mnexium handles for you:
Chat History Management
Without Mnexium, you'd need to build and maintain a database schema for conversations, implement pagination for long chats, handle message ordering, manage soft deletes, and build APIs for listing, reading, and deleting conversations. With Mnexium, you add log: true to your request and it's done. Every message is automatically stored, indexed, and retrievable via our History API.
Memory Management
Traditional memory systems require you to manually extract facts, generate embeddings, store them in a vector database, and implement semantic search. Mnexium's learn: true flag automatically extracts important information from conversations — names, preferences, facts, relationships — and stores them with semantic embeddings. When you enable recall: true, relevant memories are automatically injected into the AI's context based on the current conversation.
The Result
Our ChatGPT clone example has full conversation history, persistent memory across sessions, and semantic recall — all without a single database migration or vector store configuration. Check out the complete source code to see how simple it is.
- Automatic Memory. Set learn: true and Mnexium automatically extracts and stores important facts, preferences, and context from conversations.
- Conversation History. Enable history: true to automatically inject previous messages into context. No database setup required.
- Semantic Recall. With recall: true, relevant memories are automatically retrieved and injected based on the current conversation.
Let's build a simple chatGPT clone that remembers everything about your users. We'll use the Mnexium API to handle all the memory management automatically.
Step 1: Get Your API Key
First, sign up at mnexium.com and create an API key from your dashboard. You'll need this to authenticate your requests. Make sure to also have your OpenAI API key ready.
Step 2: Make Your First API Call
Here's a simple example using fetch. Notice the mnx object - this is where the magic happens. We're enabling logging, learning, recall, and history all in one call.
const response = await fetch("https://mnexium.com/api/v1/responses", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer mnx_live_...",
"x-openai-key": "sk-...",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
body: JSON.stringify({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
input: "My name is Alex and I love Italian food",
mnx: {
subject_id: "UUID", // The user
chat_id: "UUID", // The conversation
log: true, // Log the interaction & maintains history
learn: true, // Extract memories automatically
recall: true, // Retrieves & injects relevant memories
history: true // Include full conversation history
}
})
});💡 Rule of thumb: subject_id = the user, chat_id = the conversation.
What Happens
When you make a request to Mnexium, several things happen behind the scenes:
- History Injection — If
history: true, Mnexium retrieves the conversation history for this chat_id and prepends it to your request, giving the AI full context of the conversation. - Memory Recall — If
recall: true, Mnexium performs a semantic search across the user's memories and injects relevant facts into the system prompt. - AI Response — The enriched request is sent to your chosen model (GPT-4, Claude, etc.) which now has full context and relevant memories.
- Logging — If
log: true, both the user message and AI response are stored in the conversation history. - Learning — If
learn: true, Mnexium analyzes the conversation and extracts important facts, preferences, and context to store as memories.
Why This Matters for AI Developers
Without Mnexium, you'd need to build and maintain all of this infrastructure yourself:
- A database for conversation history with proper indexing
- A vector database (Pinecone, Weaviate, pgvector) for semantic memory
- Embedding pipelines to convert text to vectors
- Retrieval logic to find relevant memories
- NLP pipelines to extract facts from conversations
- APIs to manage all of the above
With Mnexium, you add a single mnx object to your existing OpenAI calls and get all of this out of the box. No infrastructure to manage, no embeddings to generate, no retrieval logic to tune — just AI that remembers.
See It In Action
Here's what it looks like when a user updates their preferences. The user first tells the AI their favorite fruit is apples, then later updates it to bananas. Mnexium automatically learns and updates the memory.

And here's what those memories look like in the Mnexium dashboard. You can see the extracted facts, search through them, and manage them via the UI or API.

Memory Lifecycle
Notice how the old memory ("favorite fruit is apples") was automatically superseded by the new one ("favorite fruit is bananas"). Mnexium handles memory lifecycle for you — when new information contradicts existing memories, the old memory is marked as superseded and the new one takes precedence. This ensures your AI always has the most up-to-date information without accumulating stale or conflicting facts.
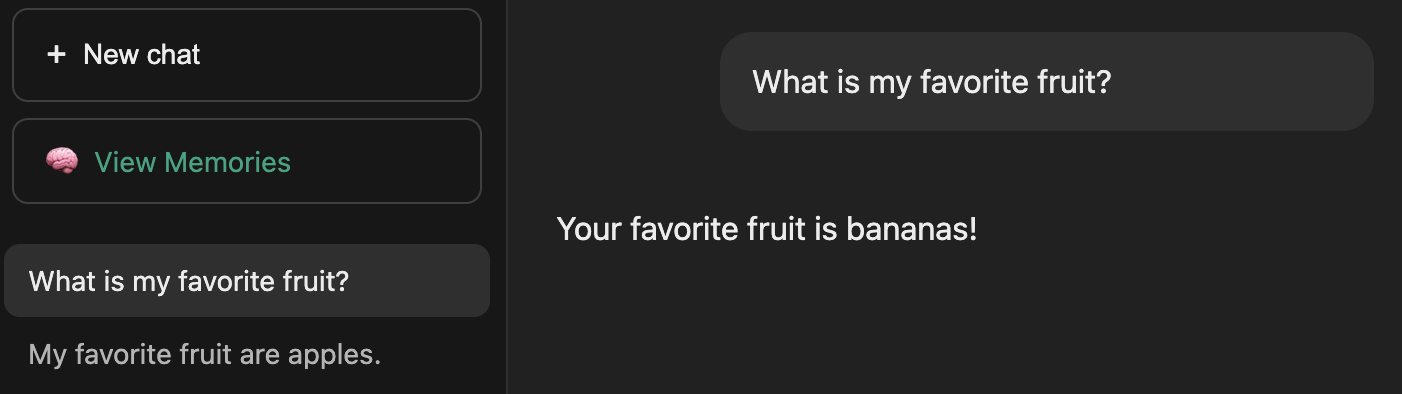
Memory Recall
In a completely new chat, when the user asks "what is my favorite fruit?" — the AI correctly recalls "bananas" from memory. This is the power of semantic recall: relevant memories are automatically retrieved and injected into context.
What's Next?
Check out our documentation to learn about more features. Define custom System Prompts per project to control AI behavior and personality. Monitor everything with Activity Logs for debugging and compliance, and use Dashboard Analytics to track memory growth, chat activity, and usage patterns.
Ready to give your AI a memory? Sign up for free and start building today.